Among many treatment options for sleep apnea, the use of assisted breathing device at home, during sleep such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and oral appliances can be considered, which are discussed below:
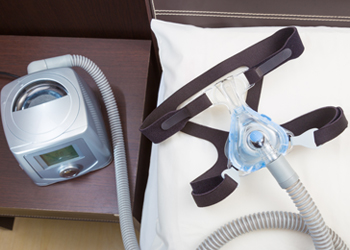
Continuous positive airway pressure
In continuous positive airway pressure, a mask is worn over the nose and throat that is connected to a motor through a tube.
The motor provides air with constant pressure and keeps the obstructed airways open. The amount of air pressure is adjusted accordingly to a person’s condition. People who use CPAP may have a decrease in daytime sleep, lower risk of heart disease and depression. Though CPAP, is a better option than other non-surgical methods for sleep apnea, people may find it uncomfortable.
Oral appliances
Oral appliances such as dental devices can help keep the blocked airways open while sleeping. These appliances are designed in accordance with a patient’s need.

Lifestyle modifications
Obese individuals should try losing weight as even shedding a few kilograms can help relieve constriction of the throat and help in preventing the symptoms of sleep apnea. Reducing weight not only helps with the symptoms of sleep apnea but may also resolve other obesity-related issues.
It is necessary to maintain a healthy weight, or else sleep apnea may return. Maintaining a healthy weight is a challenge especially for obese individuals as they tend to gain back the lost weight. Therefore, the management of weight along with a proper diet plan is essential.
Along with weight management, the following measures can also be taken:
- Avoid alcohol and some medications like sleeping pills, as they tend to relax the muscles present in the back of the throat and obstructs the airways.
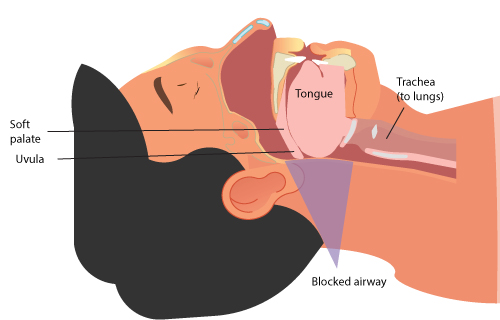
- Try to sleep on the side or abdomen rather than the back, as sleeping on the back can cause the tongue and the soft palate to rest upon the back of the throat and block the airway.
- Try to quit smoking.
Taking a healthy diet, avoiding alcohol, certain medications, tobacco, and performing physical exercises can go a long way in reducing the recurrence of obstructive sleep apnea. Physical exercises should be done in moderation and individuals should also evaluate their lipid profile so as to avoid the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Surgery to excise the excess tissue may be suggested as a last resort. The choice of treatment depends on the person’s condition and the possible after-effects.
 Obesity has now become a global problem, as it can result in many associated comorbidities including sleep apnea, which may even affect the obese children. Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that causes repeated pauses while breathing during sleep. It is mostly seen in men than in women. Snoring loudly during the night and feeling sleepy during the day, even after sleeping for adequate hours may indicate sleep apnea.
Obesity has now become a global problem, as it can result in many associated comorbidities including sleep apnea, which may even affect the obese children. Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that causes repeated pauses while breathing during sleep. It is mostly seen in men than in women. Snoring loudly during the night and feeling sleepy during the day, even after sleeping for adequate hours may indicate sleep apnea.