Obesity and its related comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus (diabesity) have become a significant worldwide problem. Obese individuals tend to show a strong relationship between their body mass index and diabetes. Although an array of treatment options are available, including oral medications and insulin injections, they are associated with adverse effects in the long run. Moreover, these treatments only control the blood sugar levels but don’t help in reducing weight.
-
Implantable devices +
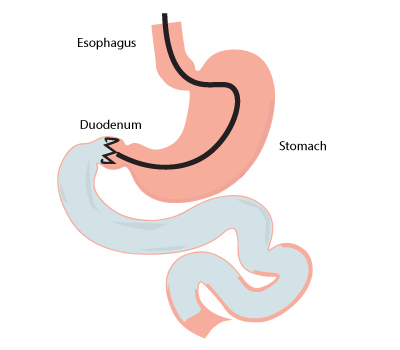
Among the latest techniques available, implantation of devices such as duodenal jejunal bypass liner can address the needs of the diabesity population worldwide. They don’t require surgery and doesn’t alter the anatomy of the gut. The duodenal jejunal bypass liner forms a physical barrier between the ingested food and the duodenum/first part of the jejunum. The duodenal jejunal bypass liners include devices such as Endobarrier.
Endobarrier is a long ultrathin flexible tube (60 cm) with a crown-like bulb at its tip. The implantation of the device in the duodenal/proximal jejunum part of the small bowel prevents the digestion of the ingested food in this area. Thereby, the absorption of nutrients occurs in the distal end of the jejunum.
-
Who is eligible for duodenum-jejunal bypass liners? +
 The procedure is used for the following individuals:
The procedure is used for the following individuals:- Obese individuals with poorly control diabetes or are not fit
for surgery - Severely obese individuals, before performing the surgery for weight loss
- Patients requiring other surgeries, to help control the blood sugar
- Obese individuals with poorly control diabetes or are not fit
-
Before procedure +
 The following measures should be taken before performing the procedure:
The following measures should be taken before performing the procedure:Diet: The patients have to follow a liquid diet for at least one week before the date of the implant. The purpose is to facilitate a clear view during endoscopy for implanting the device.
Medications: Protein pump inhibitors can be prescribed three days before the procedure.
Imaging: The upper gastrointestinal tract is examined using an endoscope to ensure individuals' suitability and to find any defects such as peptic ulcer device, as it may prevent the implantation of the device.
-
During procedure +
The patient is usually sedated before starting the procedure.
The procedure begins by introducing an endoscope through the mouth into the small bowel (duodenum). The endoscope places a guidewire as distally as possible into the duodenum. Now, a capsule containing the device is threaded onto the guidewire and placed in the pylorus (opening of the stomach into the duodenum). The capsule is positioned in such a way that the lower end sits in the duodenal bulb (the distal end of pylorus). Then the guidewire is removed and the device is released from the capsule.
The crown-like bulb gets anchored with the help of barbs in the opening of the duodenal bulb and the rest of the tube runs down into the duodenum. Now, a water-soluble contrast dye is injected and viewed fluoroscopically to confirm the positioning of the device.
The procedure takes nearly an hour to complete and the patient is discharged on the same day. The device can be removed or replaced, within a year depending on the patient’s health status.
-
After procedure +
After the procedure, a liquid diet is advised for about two weeks to minimize the risk of obstructing the liner with the food. Also, medications such as proton pump inhibitors should be continued until the device is removed to minimize bleeding. The common side effects after implanting the device include abdominal pain and nausea. But these symptoms usually resolve on its own and don’t require treatment. Rare complications include gastro bleeding and device migration.
A follow up is necessary until a year or up to the period of the removal or replacement of the device. This helps monitor the improvement in the health status of the individual and also predict the appropriate time for the removal of the device.
-
Understanding the mechanism +
After the device is implanted, the undigested food bypasses the duodenum/proximal jejunum region. However, the digestive juices of this area will mix with the food in the distal end of the jejunum. This helps in reducing the number of nutrients absorbed and also results in the increase of a hormone called glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1). GLP-1 stimulates the secretion of insulin and also inhibits glucagon, thus reducing the blood sugar levels in an obese person. The hormone also acts on the brain and increases satiety that helps to reduce weight.
-
What a patient can expect? +
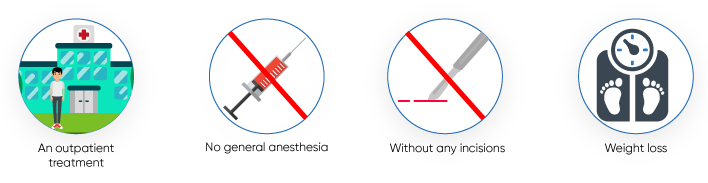
The procedure of implanting the device is safe and feasible. Also, reimplantation of the device after six months or a year helps in additional weight loss and improvement of type 2 diabetes. The other advantages of implantation of duodenal-jejunal bypass liners can be summarized as follows:
- It can be performed without administering general anesthesia.
- It is performed as an outpatient treatment.
- It is performed without any incisions.
- It helps with moderate weight loss and control of blood sugar levels by increasing satiety.
- The devices are easily removable and replaceable.
References
https://www.soard.org/article/S1550-7289(15)00021-0/fulltext
- 1