In the last couple of years, a major shift has occurred in the lifestyle of many people throughout the world. This change has made way for several diseases that are associated with obesity. Most of these individuals wish to lose weight, but the lifestyle modifications haven’t worked, and they do not wish to go under the knife. For such people, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is a good option.
-
What is Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty? +
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is a new weight loss procedure that helps to reduce the size of the stomach by using an endoscopic suturing device. ESG is different from surgical gastrectomy in a way that it can result in reduction of stomach size without a need for surgery. So, ESG holds an advantage of incision less surgery that can reduce the stomach volume by 50-60% and alter the way in which the stomach functions.
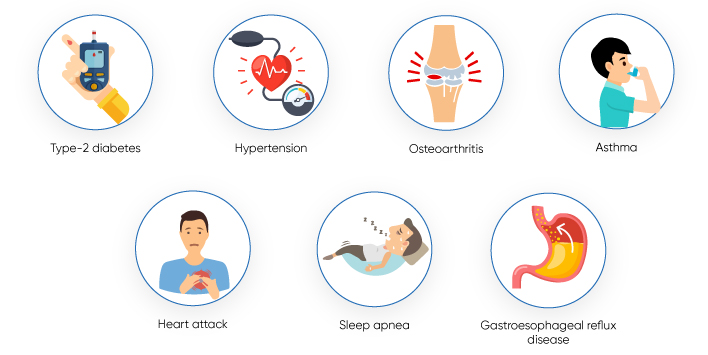
Significant weight loss can be achieved through the procedure. It can also potentially decrease the chance of occurring of other obesity related conditions that include:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Heart attack or stroke
- Sleep apnea
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
-
How does it work? +
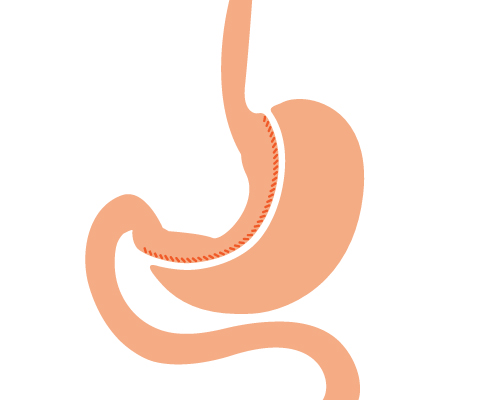
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is performed by inserting a flexible tube with a camera at one end (endoscope) through the throat into the stomach. The endoscope has a suturing device attached that places sutures (usually 12) in the stomach. These sutures alter the structure of the stomach, leaving it shaped like a tube. This shape reduces the number of calories that can be absorbed by the stomach. This in turn results in decreased weight.
-
Eligibility +
All overweight or obese people are not eligible for ESG. The physician determines the suitability of the procedure depending on the person’s condition and the expected outcomes. The eligibility for the procedure depends on the following criteria.
- The patient should be older than 18 years
- BMI >30 Kg/mg2
- Weight loss not achieved even after following medicinal therapy or lifestyle interventions
- People who are not eligible for bariatric surgery or not willing to undergo surgery
- Commitment towards long-term lifestyle changes and behavioral therapy
- Individuals without any contraindications to anesthesia
-
Pre-procedure +
The person may have to follow specific instructions given by the physician before the procedure. The person may also have to undergo tests like complete blood count (CBP) and basic metabolic panel (BMP) recommended by the physician. Any recommendations regarding food or liquid restrictions and medications should also be followed. The procedure is performed as an outpatient under general anesthesia. Antibiotics like Cefotaxime are given intravenously prior to the surgery.
-
During the procedure +
The procedure is performed using an endoscope equipped with an endoscopic suturing device. The physician advances the device through the patient’s mouth into the stomach via a protective tube to avoid any damage to the esophagus.
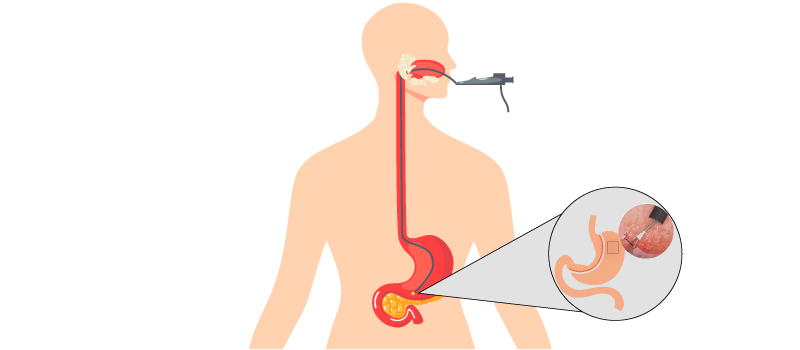
A series of sutures are made in the stomach in a specific pattern. Approximately 12 sutures are placed in the stomach. Each suture consists of six bites along the greater curvature of the stomach. These sutures are then tightened resulting in constriction of the volume of the stomach. This changes the structure of the stomach to form a tube (sleeve) shape.
The procedure takes about 1-2 hours to be completed and the patient is shifted to recovery room after the procedure is completed. It results in reduction of the volume of the stomach by 70-80%. This reduces the capacity of the stomach and helps to feel fuller quickly. The procedure also limits the amount of calories absorbed by the stomach. The duration of time that the food remains in the stomach (Gastric emptying) is also extended making the person to feel full for longer duration.
OverStitch: The OverStitch Endoscopic Suturing System helps the physician to make full thickness sutures through an endoscope. This new technology provides secure approximation of the tissue. Additionally, this system enables a wide range of less invasive solutions for the patients.
In this procedure, a sedative is injected into a vein to make the patient drowsy. Then, an endoscope along with overstitch suturing device is inserted through the mouth. It is guided up to stomach to detect any dilation of the opening into the stomach. When detected, the stomach wall is grabbed, and the sutures are placed by the device. This makes the stoma smaller and helps it return to previous post.
What makes it the top choice?
Flexibility, Interprocedural reloading, needle design, and knotless fixation are some features that make it a top choice. -
Post-procedure +
• The patient is closely monitored until he/she is conscious. The patient may be allowed to walk with help.
• The person is restricted from having anything for about eight hours post-surgery.
• The patient is explained about any specific changes in his routine medications such as to crush them and swallow during their first week post-procedure.
• Specific instructions on resuming or altering previous medications such as blood thinners, thyroid, high cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure should be followed appropriately.
• Vitamin supplements such as calcium, iron, B12, vitamin D are recommended preferably from second week.
• The patients can go home the same day or on the following day. -
Dietary recommendations +
The post-operative period is divided into three stages depending on the type of diet to be followed.
Stage I: The patient is allowed to have clear liquid diet without any added sugars for about one week after the procedure. One serving of liquid diet should not exceed 10 calories.

Stage II: The patient can have a soft diet starting from second week till the end of fourth week. It is important that the soft diet should be low in fats and sugar. It is also important that the diet should be nutrient rich. The patient should not consume water while eating semi-solid food. But the patient should take care to stay hydrated by consuming liquids between meals. Over-eating should be avoided completely.

Stage III: After four weeks the patient is allowed to return to normal diet. But it is important to stick to the dietary recommendations suggested by physician or nutritionist. The patient may have to undergo regular checkups until one year after the surgery.

-
Outlook +
The results of the procedure vary among different individuals. But, on an average the patient can lose 50% of excess weight during first six months after the procedure. The patient may also experience better management in blood sugar levels and blood pressure. But the patient’s commitment to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding lifestyle changes and dietary modifications are crucial to attain the desired success.
- 1