The procedure for different types of intragastric balloons slightly differs. Currently there are three types of intragastric balloons that are approved by FDA. They include Orbera intragastric balloon, Obalon intragastric balloon and TransPyloric Shuttle Delivery device. Other types of intragastric balloons include silimed balloon, heliosphere bag, elipse and spartz.
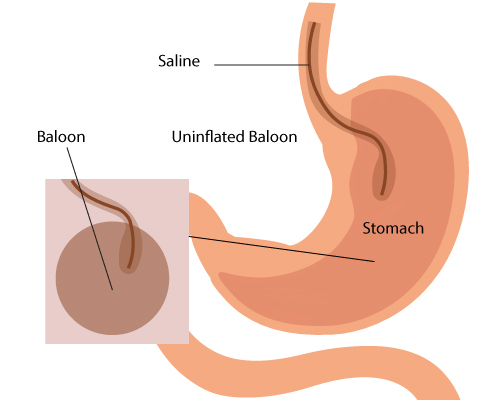
Orbera intragastric balloon: During the procedure, a thin catheter tube loaded with an elastic silicon balloon is advanced through the mouth into the stomach. Later, an endoscope is advanced in the same way to visualize the balloon. Once the balloon is placed in the position, it is inflated using saline (450-700 ml). After completing the procedure, the catheter and endoscope are removed carefully.
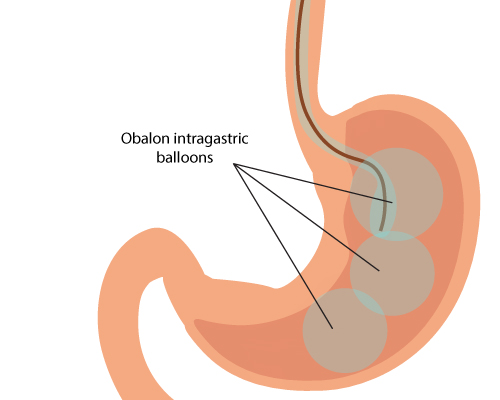
Obalon intragastric balloons: An obalon balloon is packed in a capsule with a thin catheter attached to it. During this procedure, the balloon is delivered into the stomach by making the patient to swallow the capsule, while holding the other by the physician. An ultrasound system is used to ensure that the capsule is positioned in the stomach. The balloon is then inflated with gas (250 ml of nitrogen) through the catheter. A maximum number of three balloons can be placed, in a period of twelve weeks (one for every four weeks).
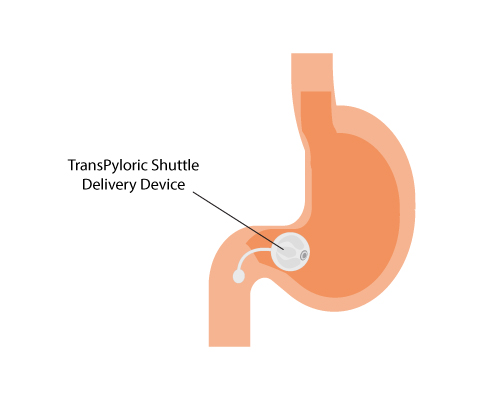
TransPyloric Shuttle Delivery Device: During this procedure, the patient is under mild sedation. This procedure is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure that is involved in placing a Transpyloric shuttle (TPS) into the patient’s stomach. Once the physician ensures the correct placement of TPS, it is inflated with a TPS controller with 900 ml of saline. This helps the TPS to take the shape of a smooth large balloon that is connected to a smaller balloon with the help of a tether. The large bulb remains in the stomach and the smaller balloon either remains in the stomach or crosses it to enter the small intestine.
The procedures may be completed within 15 to 30 minutes. The person may have to stay for few hours after which he can return home normally.